Advanced URL Filtering DSL
Introduction
To enable user to directly set up the OData filters using the Visualizer Module settings UI, we're developing a simplified syntax for defining the filters. Said syntax must be human readable and will be directly transformed into its OData counterpart to be saved in the ModuleSettings table.
Query filter syntax
A query can be composed of one or more simple expressions A operator B joined using logical operators AND, OR, NOT and enclosed in parentheses. First, here's a more complex example
contentName starts with [name] and (any contentTag equals "PC" or any contentTag equals "mac")
Expression
The left side of expression is always a field name, using the same nomenclature as Visualizer syntax. As a consequence of OData feature constraints we support the contentName and contantTags fields and the dynamic fields.
The right side of the expression can be a constant, enclosed in double quotes or query parameter, enclosed in square brackets.
Transformation to OData
A parsed query filter must be transformed to valid OData for consumption by the visualizer API. Here are some examples of said transformation for individual expressions
| Query filter expressions | OData filter expression | remarks |
|---|---|---|
| color equals "red" | details/color eq 'red' | query syntax does not need the details/ prefix |
| any of contentTags equals "PC" | tags/any(tag: tag eq 'PC') | |
| price equals 10 | details/price eq 10 | numeric constants do not need enclosing quotes |
| any manufacturer.contentSlug equals "mercedes-benz" | details/manufacturer(r: r/slug eq 'mercedes-benz') | dot notation like in visualizers. currently only slug is suppported for reference object fields |
| date greater than "2017-10-10" | details/date gt DateTime'2017-10-10' | dates must use ISO format. transformation must include type cast |
| any of categories equals "RPG" | details/categories/any(c: c equals 'RPG') | it's possible to write either any or any of |
| color equals [color] | details/color eq '[color]' | parameter don't need enclosing quotes |
| color not equals "blue" | details/color ne "blue" | negation translates into specialized operators |
| contentName starts with "[OT]" | startswith(name, '[OT]') | startswith function. note that right hand value is enclosed in quotes making it a literal not a query parameter |
Transforming operators
| query filter operator | OData operator |
|---|---|
| equals | eq |
| not equals | ne |
| greater than | gt |
| greater than or equal | ge |
| less than | lt |
| less than or equal | le |
Formal grammar
Below is the grammar of the query DSL written in Augmented Backus-Naur Form.
QueryFilter = Expression 1*LWSP *(LogicalOperator 1*LWSP Expression)
Expression = "(" QueryFilter ")" / RootExpression
LogicalOperator = "and" / "or"
RootExpression = [ AnyModifier 1*LWSP ] FieldAccessor 1*LWSP Operator 1*LWSP ( Variable / Constant )
AnyModifier = "any" / "any of"
Operator = "starts with" / ArithmeticOperator
ArithmeticOperator = [ "is" 1*LWSP ] [ "not" 1*LWSP ] "equal" [ "s" ]
ArithmeticOperator =/ "greater than" / "greater than or equal"
ArithmeticOperator =/ "less than" / "less than or equal"
FieldAccessor = Identifier [ "." Identifier ]
Constant = Number / StringLiteral
Number = [ "-" ] *DIGIT [ "." 1*DIGIT ]
StringLiteral = """ 1*CHAR """ / "'" 1*CHAR "'"
Variable = "[" Identifier "]"
Identifier = ALPHA *(ALPHA / DIGIT)
Example
1) In Content Library, create 5 content items of Person content type:
| First Name | Last Name |
|---|---|
| Ben | Zhong |
| Dinesh | Kumar Karmankar |
| Mike | Bigun |
| Manuel | Gonzalez |
| Daniel | Aguilera |
2) Create a blank page and add following Visualizer:
| Type | List |
| Content Type | Person |
| Visualizer | Square image Right w/ Name |
3) In the visualizer settings screen, enable URL Filtering:
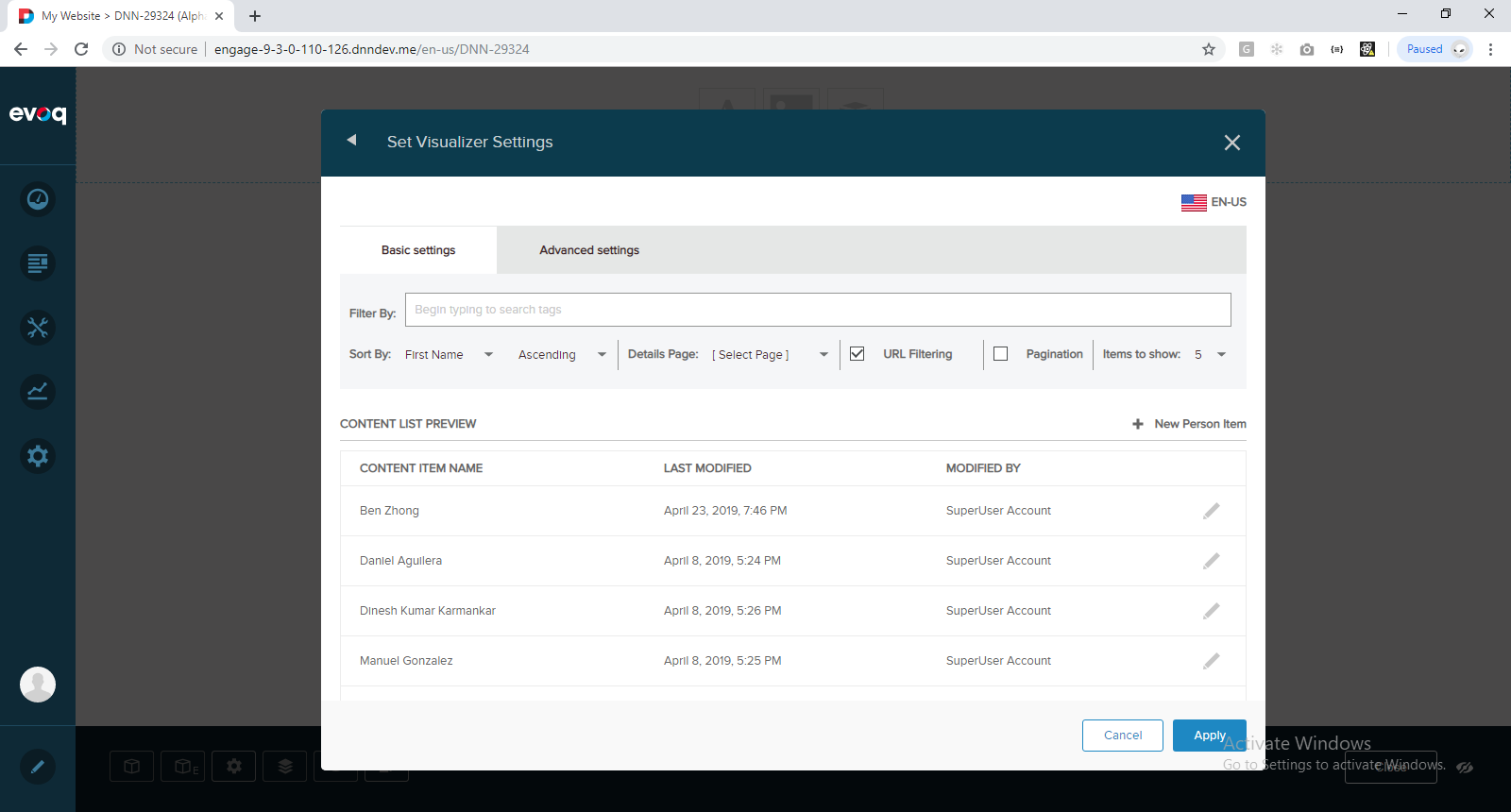
4) Click Advanced Settings and enter following filter expression:
firstName equals 'Manuel'
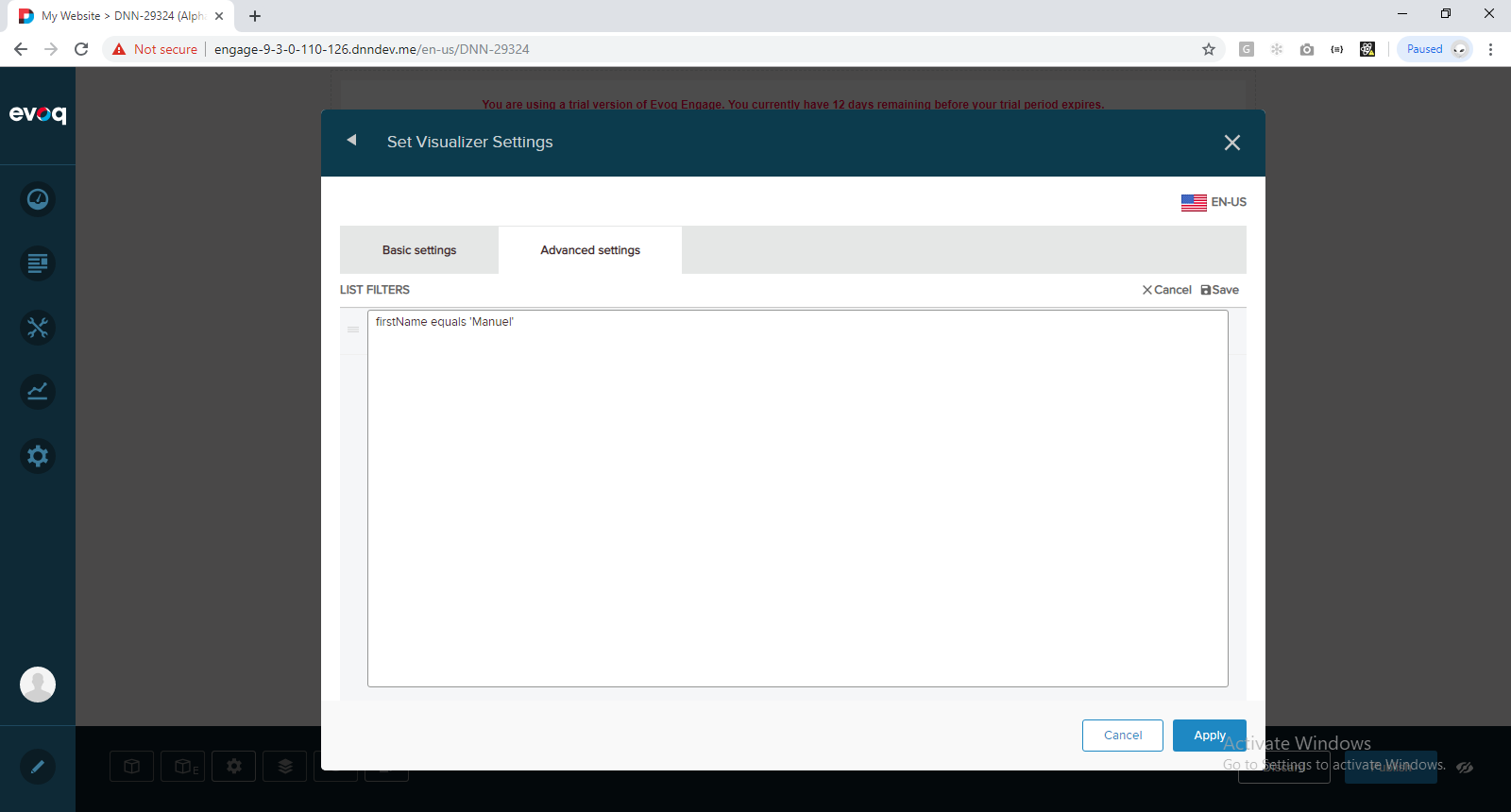
5) Click Save and then Apply. Page should look like this:
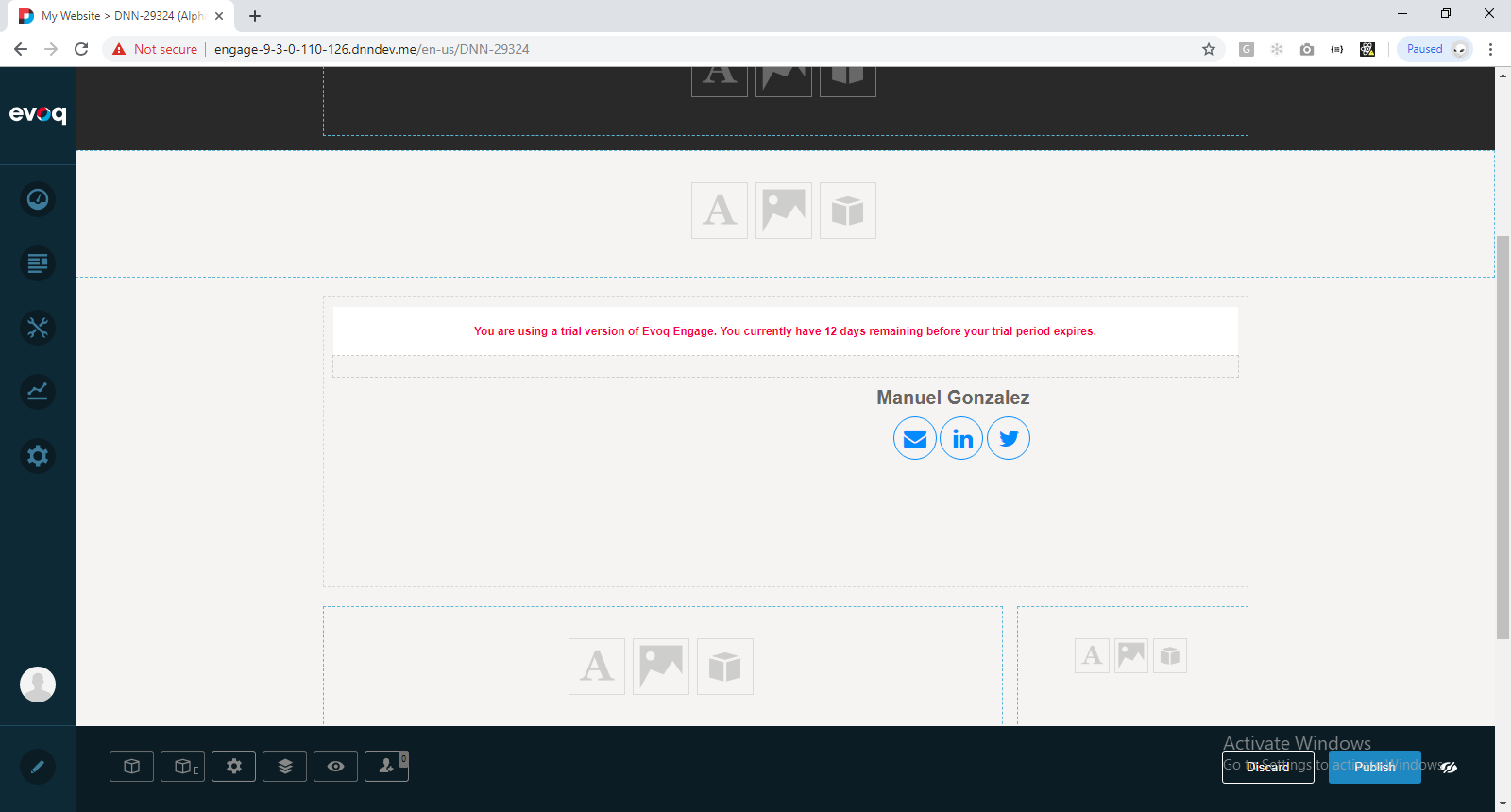
6) Hover the visualizer and click Manage Visualizer Settings:
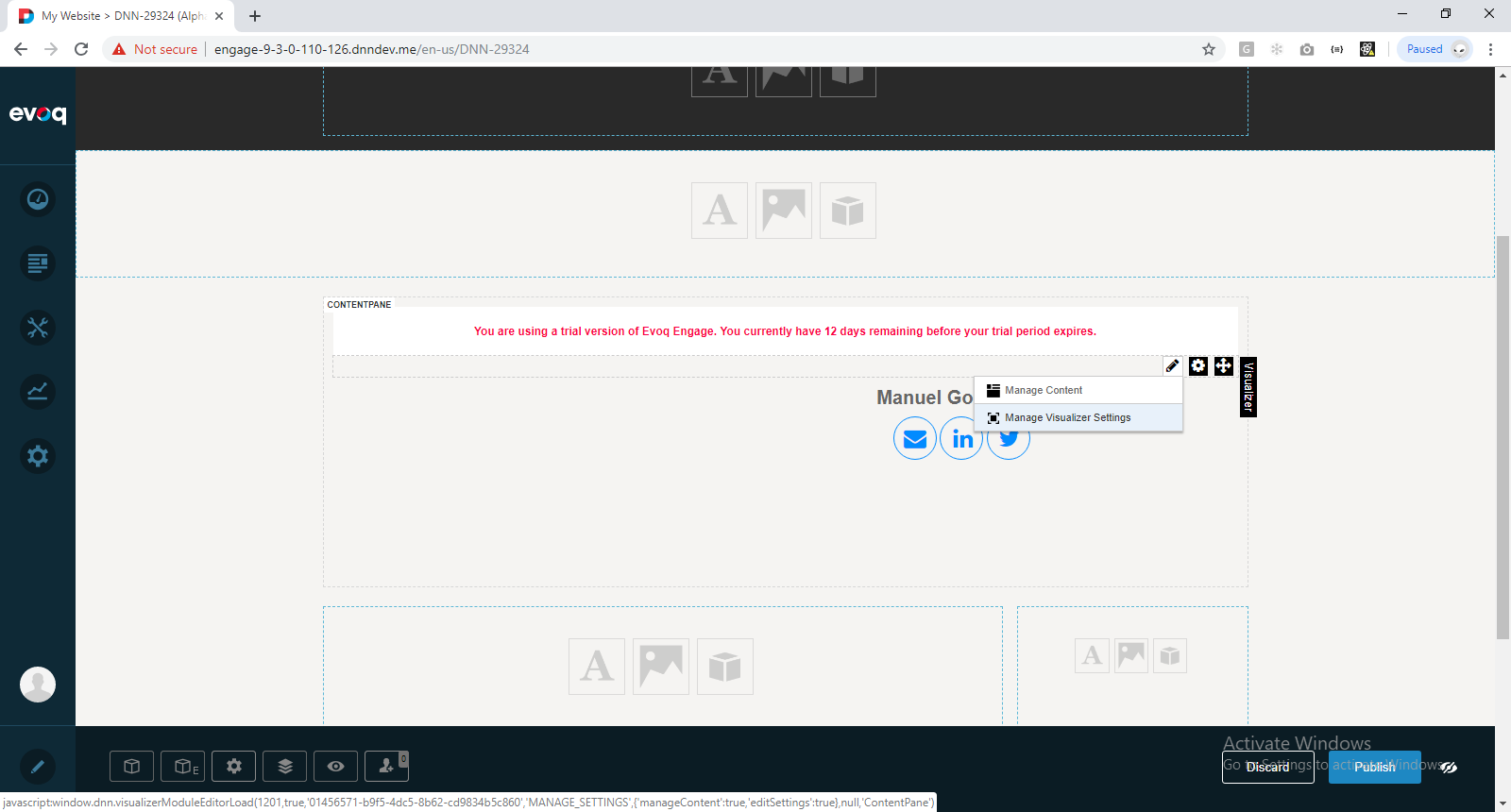
7) Click Next on all steps of the wizard up to the Set Visualizer Settings page. Click Advanced Settings and change the filter expression to:
firstName equals 'Dinesh'
8) Click Save, and then Apply. The visualizer will now render a new person based on above criteria.
Processing query filters
The user can create multiple filters for a given Visualizer Instance. They will be stored as-is along other module settings. When the Visualizer Instance is saved, the service validates the syntax and also the use of fields (ie. all fields names exist in the content type) as well as correct use of data types to ensure that numeric field isn't compared to strings and date fields are used with properly formatted dates.
Here's a sequence diagram describing that interaction:
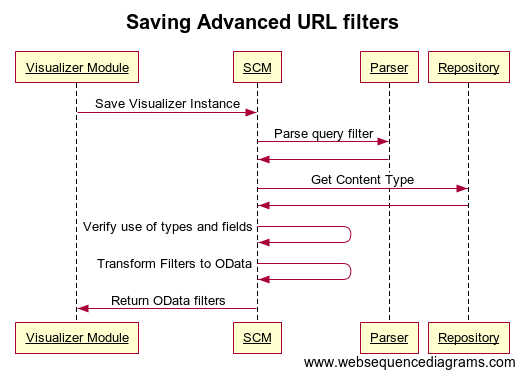
Validating query against the queried Content Type
After being successfully parsed, a query filter must be validated against the queried Content Type. Here are rules governing content type fields
Number field
Can only be used with numbers
Valid examples
field equals 5
Invalid examples
field equals "a"
field equals "5"
Date field
Can only be used with properly formatted ISO date.
Valid examples
date equals "2017-10-10"
date less than "2018-01-01T10:20:10"
Invalid examples
date equals "2017/09/07"
Date field (sub-type time)
Can only be used with a properly formatted time string
Valid examples
time less than "10:10:00"
time equals "12:00"
Invalid examples
time equals "99:00"
time less than "noon"
Reference object field
- Equality operators cannot be used with reference object fields
- Only slug is allowed when querying reference object fields
- Single ref can use dot notation to access slug
- Multiple ref must use any (of) modifier
- starts with cannot be used with ultipl
Valid examples
singleRef.slug equals "my-page"
any multipleRef.slug equals "my-page"
Invalid examples
singleRef equals "some id"
multipleRef.slug equals "my-page"
singleRef.name equals "Tomasz"
any multipleRef.slug starts with "my-page"
Multiple choice field
Can only be queried with conjunction the any of modifier.
Cannot be used with starts with.
Valid example
any of choices equal "YES"
any engineType equals "diesel"
Invalid examples
engineType equals "diesel"
any of choices starts with "medium"
Extracting query string parameters
The query syntax allows two types of values to be used: constants and variables. The latter are alphanumeric identifiers enclosed in square brackets. For example the expression below uses a variable name.
contentName starts with [name]
When such variable is parsed it will be transformed into a query string variable in the OData filter definition as defined.
[{"QueryStringParams": ["name"], "ODataFilterQueryFormat": "name eq '[name]'"}]
Note that a variable must not be enclosed in quotation.
If a query is written as follows
threadTitle starts with "[OT]"
Then the value "[OT]" will be used as a plain string literal, and will not generate a query string parameter:
[{"QueryStringParams": [], "ODataFilterQueryFormat": "details/threadTitle eq '[OT]'"}]